Reducing latency in business networks
Latency is a key metric of the real-time performance of a connection, process, or online service. It is commonly used by businesses to monitor and optimise network and application performance.
Whether it’s to understand the performance of a firewall, broadband connection, or cloud service, latency is widely used because it is simple to measure and interpret.
This guide explains latency, why it matters for businesses, and how to measure and reduce it to improve network and application performance.
Contents
- What is latency?
- What causes high latency?
- The impacts of high latency on businesses
- Measuring and interpreting latency
- Low latency thresholds
- Reducing latency in your business network
What is latency?
Latency represents the time it takes for requested actions to complete, such as how quickly a website loads, a VoIP call connects, or data is retrieved from a cloud service. It measures how responsive applications, services, and network connections are to user requests.
Latency is measured in milliseconds (“ms”, as per diagram below), and fluctuates due to factors like network congestion, available bandwidth, and even weather conditions in wireless connections.
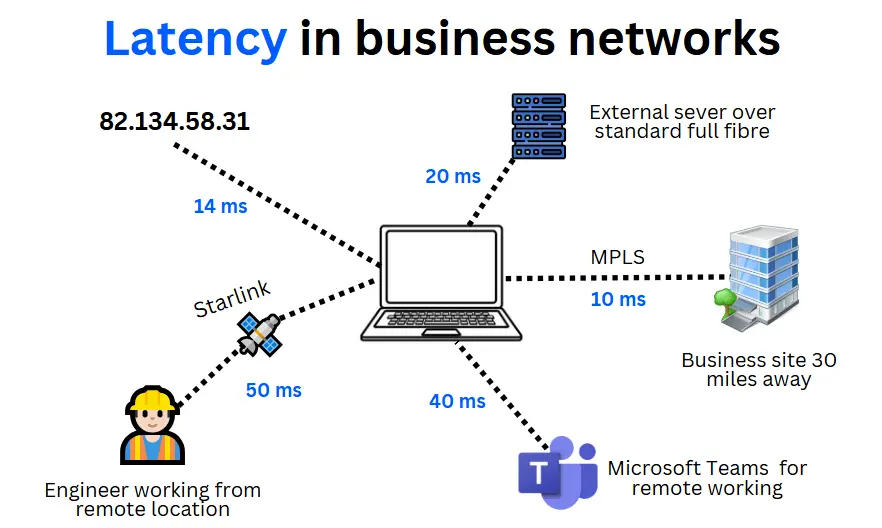
Lower latency means faster responses, ensuring smoother performance. This is especially important for real-time applications, like VoIP, video calls, and cloud computing.
A useful way to think about latency is like a journey estimate on Google Maps. The time it takes to travel from point A to point B depends on factors like traffic congestion, road speed limits, and tolls, just like network latency depends on routing, congestion, and bandwidth.
What causes high latency?
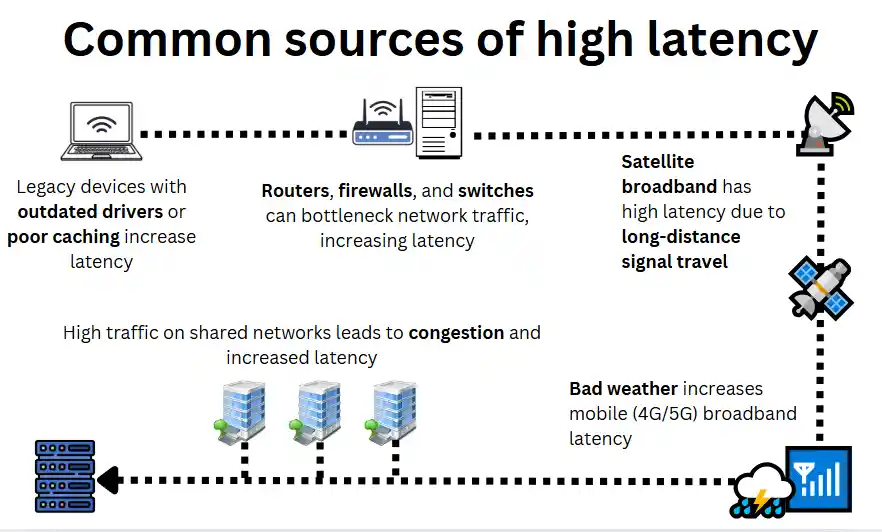
High latency occurs when data takes longer than expected to travel between your device and an online service.
Multiple factors contribute to high latency, including network hardware, broadband type, software processing, and congestion. Below are the most common causes of latency and how they impact performance.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Travel distances | Longer travel time increases delay. The farther data must travel (e.g., across continents, via satellites, or through multiple network points), the longer the transmission time. This highlights the importance of DNS setups to make sure the closest servers are being used. |
| Congestion | Too many users, too little bandwidth. When network demand exceeds available bandwidth, data packets experience queuing delays. This happens in crowded networks, peak hours, and contested (shared) broadband connections. |
| Complex routing | More stops, more delays. Data passes through multiple routers and switches. Each additional hop requires processing time, increasing latency. Inefficient routing paths (e.g., international detours) worsen this. |
| Inefficient hardware | Slow devices slow everything down. Routers, modems, servers, and network switches process and forward data packets. Outdated or overloaded hardware introduces delays. Similarly, slow servers increase response times. |
| Wireless broadband | Unstable signals increase delay. Wireless networks (WiFi, 4G, 5G, satellite) are affected by obstacles, weather, and interference. Poor signal strength leads to retransmissions, increasing latency. |
| Encryption | Extra data handling adds time. Some network protocols (e.g., TCP, VPNs, SSL encryption) require extra processing steps, increasing response time. This overhead is more noticeable in encrypted or secure networks. |
| Throttling | Artificial speed limit reductions. Broadband providers intentionally slow down certain types of traffic (e.g., video streaming, downloads) to manage congestion, even when the connection is capable of higher speeds. |
For a deeper analysis, see our breakdown for business networks here.
The impacts of high latency on businesses
High latency means data takes too long to reach its destination, preventing applications from working as intended.
For instance, UCaaS video calls become choppy if latency exceeds 50 milliseconds, and stock market transactions can be delayed if it goes above 10 milliseconds.
The impact of high latency depends on the application, but it always creates a performance bottleneck. Whether it slows down employees using third-party services or frustrates customers accessing your online services, the consequences can be significant:
- Reduced employee productivity: Slow applications such as unreliable logistics tracking, sluggish SaaS tools (CRM, ERP) and low quality VoIP calls waste employee time, cause delays and errors, and reduce operational efficiency.
- Poor customer experience: Slow-loading websites, buffering video content, and long checkout times in e-commerce frustrate customers, reduce engagement, and damage your reputation.
- Security risks: High latency in cybersecurity SaaS (e.g., fraud detection, intrusion prevention) delays real-time alerts, increasing vulnerability to security threats.
Ultimately, high latency leads to financial losses. High latency signals problems in your network, whether from your internal setup, business broadband provider, or SaaS applications.
Measuring and interpreting latency
Technically speaking, latency is the time in milliseconds it takes for a small data packet to travel from a device to a server and back. This is commonly referred to as Round-Trip Time (RTT).
However, latency measurements vary depending on the purpose. It’s different for quick testing, in-depth diagnostics, or long-term monitoring.
Measuring techniques
There are three main ways to measure latency, depending on what you need:
Ping command
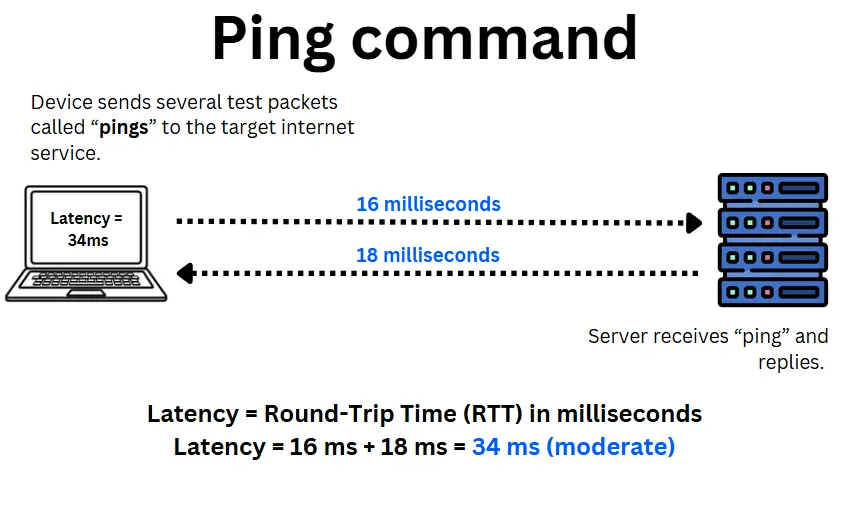
Also known as ICMP Echo Request, Ping is the most commonly used method to measure latency. It provides a quick estimate of the response time between your device and a specific server.
It sends a small data packet to the target server, which replies. The test runs multiple times to provide a minimum, average, and maximum latency value and packet loss data.
However, Ping only measures total round-trip latency. It does not show where delays occur along the route or provide insights into performance over time.
Try it by opening your command line and typing “ping www.website.com” or “ping 141.193.213.10” to get instant latency results.
Traceroute
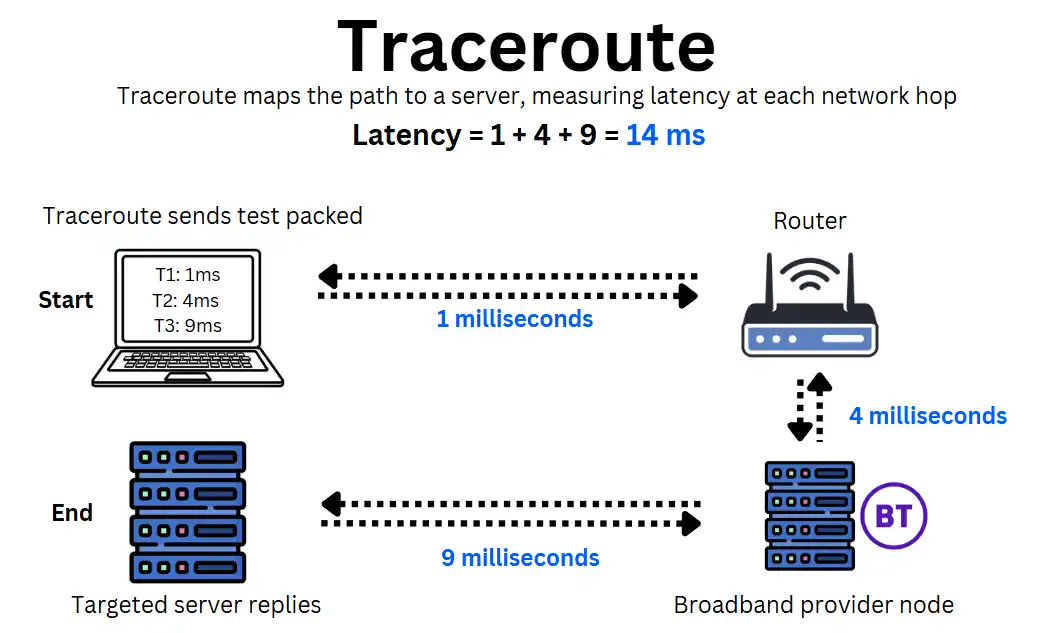
Traceroute is a step up from Ping, measuring delays at each hop along the network path. This helps identify whether your local network, provider, or an external service provider causes latency.
It works by sending data packets to a destination while tracking response time at every step along the way.
Try it yourself by by typing “tracert www.website.com” on Windows or “traceroute www.website.com” on the Mac/Linux command line.
Latency monitoring with third-party apps
For continuous latency monitoring, businesses use third-party network monitoring tools that offer real-time insights, historical data, and automated alerts.
Unlike Ping or Traceroute, these tools provide ongoing analysis and visual dashboards to track trends, diagnose recurring issues, and ensure SLAs (Service Level Agreements) are met.
Other performance indicators
Other indicators are necessary to tell the full story of network performance. These include:
- Jitter: Measures variability in latency between packets. High jitter causes unstable VoIP calls, video buffering, and inconsistent response times despite low latency.
- Packet loss: The percentage of data packets that never reach their destination. Even low latency won’t help if packets keep dropping, causing lag, voice dropouts, or slow-loading applications.
- Speeds (bandwidth): A low-latency connection can still feel slow if it lacks sufficient bandwidth. Test your business broadband speed (bandwidth) to ensure fast, reliable performance.
Together, these metrics give a full picture of network health, helping businesses diagnose issues, optimise applications, and meet service expectations.
Low latency thresholds
Understanding what “acceptable latencies” are for each application is key when procuring software and designing your network.
Even with a well-designed network, latency thresholds can’t always be met due to external factors. However, a strong setup significantly improves your chances of maintaining low latency for each application.
For example, financial institutions conducting high-frequency trading are more likely to maintain latency under 5 milliseconds by using dedicated fibre broadband with broadband failover, network load balancing and SD-WAN.
On the other hand, a smaller business that primarily relies on video conferencing will likely be satisfied with latency under 50 milliseconds, which can be achieved with fibre optic business broadband or low-orbit satellite solutions like Starlink.
Here are typical latency thresholds for a wide range of common and niche applications, including the impacts of exceeding these thresholds:
Low latency thresholds
| Application | Acceptable Latency | Impacts of Exceeding Threshold |
|---|---|---|
| VoIP | < 50 ms | Poor call quality, echoes, dropped calls. |
| Video calls | < 50 ms | Lag, poor video/audio quality, disrupted communication. |
| Web browsing | < 100 ms | Slow page load times, poor user experience. |
| General cloud apps (SaaS, storage, collaboration) | < 100 ms | Slow data retrieval and processing, reduced productivity. |
| Standard financial transactions (banking, retail payments) | < 50 ms | Delays in processing, customer frustration. |
| Real-time trading (forex, stock market transactions) | < 20 ms | Delays in trade execution, potential financial losses. |
| E-commerce checkout | < 100 ms | Slow transaction processing, cart abandonment, lost sales. |
| Streaming services | < 100 ms | Buffering, reduced video/audio quality, interrupted playback. |
| Consumer IoT (smart home devices, voice assistants) | < 50 ms | Delayed device responses, reduced automation efficiency. |
| High-frequency Trading (HFT) | < 5 ms | Delays in trade execution, significant financial losses. |
| Autonomous vehicles | < 10 ms | Safety risks, delayed responses, potential accidents. |
| Augmented Reality (AR) | < 20 ms | Lag in visual overlay, reduced user experience and immersion. |
| Virtual Reality (VR) | < 20 ms | Motion sickness, disorientation, poor user experience. |
| Telemedicine (Remote surgery) | < 20 ms | Delays in remote control, risks to patient safety. |
| Industrial automation | < 20 ms | Inefficiency, potential equipment malfunction, safety hazards. |
| Smart grid management | < 50 ms | Delays in response, inefficiencies in power distribution. |
Reducing latency in your business network
Latency arises at many points in your network, so reducing it requires an understanding of how and where it arises and by how much. This section explains how to reduce latency at each level of your network:
- Local network (LAN) latency
- Broadband latency
- Wide network (WAN) latency
- DNS and Content Delivery latency
- Application and server latency
Local network (LAN) latency
Latency contribution: <5 milliseconds for optimised cable-only LANs; 100+ milliseconds for poorly configured LANs.
This includes switches, load balancers, internal firewalls, and WiFi. While LAN latency is usually low due to short distances, factors like poor cabling, congested switches, slow firewalls, and outdated WiFi setups can make it a major bottleneck.
Reducing LAN latency
- Using wired Ethernet where possible: It provides lower and more consistent performance than WiFi.
- Upgrade network switches and routers: Older equipment introduces delays, especially under high traffic loads.
- Enable Quality of Service (QoS): Prioritise latency-sensitive applications like remote VoIP and video calls over less urgent traffic.
- Reduce firewall processing delays: Overly complex security policies and slow firewalls can increase packet processing time.
- Optimise WiFi performance: Use WiFi 6, minimise interference, and ensure coverage through mesh networks and Guest WiFi.
- Check for network congestion: Identify and resolve overloaded switch ports, business broadband routers or misconfigured VLANs.
Broadband latency
Latency contribution: <5 milliseconds for dedicated leased lines, 100+ milliseconds for DSL or geostationary satellites.
Your broadband technology and network provider play a significant role in latency performance. While leased line technology offers the lowest latency, shared bandwidth broadband connections can cause delays due to congestion and unsuitable providers may not have the cloud connections you require.
Here is the latency of all broadband connections available to UK businesses:
| Broadband technology | Latency (ms) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| GEO Satellite (Traditional business satellite broadband) | 500-800 | Extremely high latency. Signals travel ~36,000 km to geostationary satellites, causing significant delay. |
| LEO Satellite (Starlink/OneWeb) | 25-60 | Lower satellite latency. LEO satellites are much closer (~550-1200 km), reducing signal travel time. |
| ADSL | 24 - 28 | Highest wired latency. Copper wiring degrades signals over distance, increasing response times. |
| Business mobile Broadband (4G/5G) | 5-50 | Variable latency. Wireless signals are affected by interference, signal strength, and network congestion. |
| SoGEA | 10-14 | Moderate latency. Uses a mix of fibre and copper, which introduces some delays. |
| Virgin Cable Broadband | 12-15 | Moderate latency. Coaxial cables reduce signal loss but still rely on some copper infrastructure. |
| Full fibre business broadband | 4 - 8 | Low latency. Uses fibre optics, but shared network traffic can introduce slight fluctuations. |
| Wireless leased lines | 2 - 15 | Low but variable latency. Uses microwave or millimeter-wave radio signals, which can be affected by weather and interference. |
| Leased line broadband | 2 - 5 | Lowest wired latency. Dedicated, uncontended fibre ensures ultra-stable and minimal latency. |
Reducing broadband latency
- Upgrade to dedicated fibre: If available and affordable, upgrade to a dedicated leased line as this gives the lowest possible latency.
- Choose a provider with low-latency peering: Each provider (e.g., BT, Sky, TalkTalk) has different routing agreements and direct connections to cloud services, reducing unnecessary hops.
- Avoid satellite broadband for low-latency apps: Satellite internet, especially geostationary satellites (GEO) can become the single highest source of latency (500ms+) due to long distances.
- Check for throttling: If you’re a home-based business relying on residential broadband, upgrade to a business broadband deal to avoid bandwidth throttling.
Wide network (WAN) latency
Latency contribution: <5 milliseconds for dedicated dark fibre or MPLS links; 100+ milliseconds in poorly integrated cloud services.
A significant portion of latency arises at the wide area network (WAN) level, which is the network made up of your business sites, remote workers and external cloud services.
WANs are complex, but latency usually arises due to:
- Poor routing decisions (too many hops, suboptimal network paths).
- Congested links (shared bandwidth without prioritisation, lack of load balancing)
- Poorly integrated cloud services
Reducing WAN latency
- Implement SD-WAN: Dynamically selects the fastest, least congested path for traffic.
- Opt for dedicated links: Dark fibre and MPLS provide fast, stable inter-site connections.
- Peer directly with cloud providers: AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer direct private connections to cloud storage and computing to reduce latency.
- Optimise VPN: Ensure encryption isn’t adding unnecessary delays.
DNS and CDN latency
Latency contribution:<5 milliseconds for optimised CDNs; 100+ milliseconds for poorly configured DNS setups.
DNS and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) affect the speed at which websites and cloud services load. Slow DNS resolution, DNS hosting and lack of CDN caching can introduce employee and customer delays.
DNS and Content Delivery Networks (CDNs) affect how quickly your network resolves domain names and loads web-based services.
Slow DNS providers, lack of CDN caching, poor DDNS providers, and overloaded servers will increase the latency of your employees trying to access external services and your customers trying to reach your digital offerings.
Reducing DNS and Content Delivery latency
- Use a fast DNS resolver: Services like Cloudflare (1.1.1.1) or Google DNS (8.8.8.8) usually resolve queries faster.
- Host digital services with high-performance DNS: Poor DNS hosting increases website latency.
- Use a Content Delivery Network: CDNs store copies of websites and apps closer to users, speeding up loading times.
- Use DDNS for self-hosting: Can use Dynamic DNS to self-host at very low cost on any small business broadband connection.
Third-party server latency
Latency contribution:<5 milliseconds for optimised cloud infrastructure; 100+ milliseconds for overloaded or poorly designed services.
Even with a fast network, delays can occur if third-party cloud services are slow. Delays can be caused by overloaded cloud servers, slow database queries and inefficient backend processing times at the cloud level.
This includes services like business VoIP phone systems.
Reducing third-party server latency
- Choose reputable cloud providers: Opt for data centres with low-latency infrastructure near users.
- Work with a Managed Service Provider: They manage third-party services and ensure SLAs are met.
Latency – FAQs
Our business broadband experts answer frequently asked questions regarding latency in business broadband in the UK:
What is the difference between latency and speed?
Broadband speed refers to bandwidth or how much data can be transmitted at once. Latency, on the other hand, measures how long it takes for data to travel between two points.
While speed (bandwidth) affects how much data you can send or receive at a time, latency determines how quickly a request is processed. This makes latency a better measure of real-world connection responsiveness.
What is “good” latency?
“Good” latency simply means low latency, which ensures online applications and services perform smoothly.
However, latency requirements vary. What’s acceptable for web browsing may be too high for real-time applications like business VoIP integrations, video conferencing, or financial transactions. See a list of typical thresholds here.
How do businesses run ultra-low latency applications?
To achieve the lowest possible latency, businesses usually host services locally (on-premise servers) or establish high-performance inter-site connections with dark fibre or MPLS links.
This is because most latency originates externally, beyond the local business network or outside a high-performance Metro business Ethernet network.
Low-latency applications include high-frequency financial trading (with businesses forming high-performance links with trading servers) and industrial automation where real-time responses are needed from IoT machinery and sensors.

