SD-WAN
Future-proof your business’s interconnectivity and scalability
Get an expert opinion today…
Future-proof your business’s interconnectivity and scalability
Get an expert opinion today…
SD-WAN simplifies the management of your business’s inter-office network and improves its performance by routing internet traffic over the most efficient path. It’s safe, conveniently controlled from the cloud, and can incorporate multiple broadband technologies like fibre-optics, LTE and satellites.

These include its virtual network overlay, comprehensive security features, and cloud-based management environment.

SD-WAN offers the best value for money when managing a WAN. It’s high performing, scalable, backwards-compatible, and has in-built redundancy as well as fantastic UX.

You can acquire the service directly from big providers like Cisco and Palo Alto Networks or through a managed service provider in the UK.
SD-WAN (Software-Defined Wide Area Network) is a powerful internal telecommunications method used by businesses, enterprises, and institutions with resources dispersed across a wide geographical area.
Instead of using expensive, privately owned cables to pass encrypted internal communications from one site to another, SD-WAN uses any shared telecoms network. The SD-WAN software dynamically adapts the data’s route to ensure it takes the fastest path between sites.
It is the internal communications equivalent of Google Maps, which can help you choose the fastest route possible for your trip or commute, using all the means of transport available and your personal choices.
SD-WAN has only become possible because of technological improvements in cloud storage, fibre-optic broadband, and cybersecurity essentials, just to name a few.
SD-WAN is very capable software invented to simplify and optimise the management of a business’s WAN (Wide Area Network) using shared, public, and private telecoms networks.
It’s akin to your employees using “Google Maps” or “Ways” to optimise travelling from one site to another on shared roads, rail and walkways.
However, to truly understand it, we must explain the concept of WANs and where SD-WAN fits in its historical context.
A WAN, or Wide Area Network, is any telecommunications network that extends over a large geographical area, safely and efficiently connecting many smaller local networks (LAN).
An enterprise WAN is one where all its premises and digital assets are safely and efficiently interconnected, no matter how geographically dispersed. This includes interconnecting branch offices, physical and cloud servers, warehouses, etc.
💡WAN disambiguation. Copper-wire telephone and fax networks, and even the World Wide Web, are types of WANs. However, the term typically refers to any sub-network within the internet, such as a business intranet or a university’s internal network.
Traditionally, big enterprises and institutions used MPLS (Multiprotocol Label Switching) to create a WAN between their offices or campuses.
This involves laying dedicated, private cables interconnecting each site, which allows for reliable, safe, and performant telecommunications but comes at a very high cost.
Most SMEs would be content with LANs within their offices and unique VPN connections or other alternatives for inter-branch communications.
However, the growth of state-of-the-art fibre-optic and mobile business broadband networks over the past 20 years made creating safe and efficient WANs over the public network possible.
Enter SD-WAN, which uses specialised software to dynamically route encrypted enterprise intercommunications over any available network, be it private leased lines, full-fibre networks, satellite broadband, or anything else.
💡 Exponential Growth: Around 60% of enterprises are using SD-WAN in 2024, compared to around 30% in 2020. Source: Palo Alto Networks
Let’s summarise the key differences between SW-WAN, MPLS and VPNs to make sure you understand the key differences and benefits of SD-WAN:
| Feature | SD-WAN | MPLS | VPN |
|---|---|---|---|
| Network Type | Uses public internet to create secure connections | Uses dedicated, private lines | Uses public internet to create secure connections |
| Software | Yes, uses software to manage and optimise traffic | No, relies on hardware-based management | Yes, uses software to create encrypted tunnels |
| Management | Centralised, often cloud-based | Managed by network provider | Centralised, often cloud-based |
| Cost | Generally lower, uses cheaper internet options | Higher, uses expensive dedicated lines | Lowest cost |
| Performance | Dynamic, optimises paths in real-time | Consistent, with guaranteed performance | Variable, depends on internet quality |
| Security | Built-in security features (encryption, firewalls) | Secure due to private lines, but may need additional measures | Secure with encryption, but depends on internet connection |
| Scalability | Easily scalable, add connections quickly | Slower to scale, requires physical infrastructure changes | Easily scalable, add more VPN connections as needed |
| Flexibility | Highly flexible, uses multiple types of connections | Inflexible, limited to private lines | Flexible, can connect from anywhere with internet |
| Reliability | High, with redundancy through multiple connections | High, but relies on dedicated paths | Variable, depends on internet reliability |
| Current uses | Ideal for businesses needing cost-effective, scalable, and centrally managed networks | Best for businesses with a critical requirement for high performance and reliability | Suitable for remote access, temporary pop-up sites, small branch offices. |
SD-WAN has five key features that differentiate it from other solutions:
The SD-WAN software is typically installed and hosted in a cloud server so administrators can configure, monitor, and manage the network from any location with cloud access.
Being cloud-based also allows the software to oversee the entire network from a centrally controlled location. The image below summarises this well:
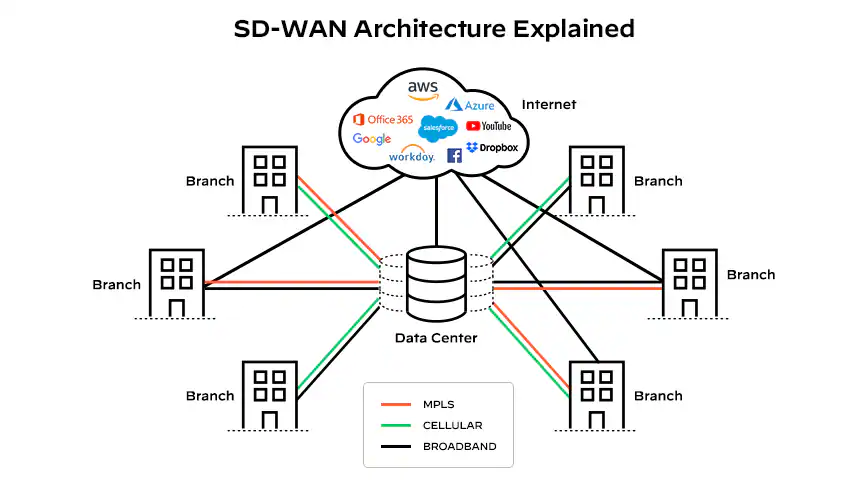
A typical enterprise, cloud-based, SD-WAN deployment. Note how traffic is routed to the different branches across any available infrastructure (MPLS, cellular, broadband). Source: Palo Alto Networks
SD-WAN creates a virtual layer on top of existing physical network connections (such as broadband, LTE, fibre, and MPLS).
This virtual layer allows the software to receive performance data for each available connection to manage and direct traffic more intelligently.
Monitoring the state of all available connections can automatically route traffic along the best path, ensuring critical applications get the bandwidth and low latency they need.
SD-WAN can identify different types of applications and prioritise them. Important applications like supply chain management and project management software, video conferencing, VoIP calls, real-time data analytics, e-commerce transactions, and operation of IoT devices get higher priority over less critical ones like regular web browsing.
While this is possible in other systems like MPLS, adjusting priorities is much more complicated. Cloud-based VPN services don’t have the functionality for such granular traffic management.
SD-WAN has built-in security features, such as encryption, firewalls, and secure internet access, to ensure the security of internal communications passing through shared broadband networks. Here are a few details:
SD-WAN uses techniques like data deduplication, compression, and caching to reduce the amount of data that needs to be sent, leaving bandwidth for other tasks. Here are more details on each technique:
The benefits of SD-WAN compared to other technologies are clear in this comparative table.
However, it’s easier to spell them out one by one:
SD-WAN uses existing, widely available internet connections, such as fibre-optic networks, coaxial cables, cellular networks, and satellites, instead of relying solely on expensive dedicated lines like MPLS.
SD-WAN can achieve performance comparable to dedicated or leased lines by dynamically routing traffic based on real-time conditions, such as latency, jitter, and bandwidth availability.
This ensures that critical applications receive the necessary resources for smooth operation. This design has in-build broadband redundancy, meaning it is more resilient than a dedicated line with a single point of failure.
It can incorporate redundancy at the business broadband provider level by routing traffic segments across networks run by distinct providers. This is key to avoiding bandwidth throttling and other traffic management limitations imposed by these.
SD-WAN integrates advanced security features, including end-to-end encryption, firewalls, and secure direct internet access. See here for more details.
These built-in protections ensure that data is secure as it travels across various shared connections, addressing potential vulnerabilities inherent in public internet use.
While VPNs offer strong encryption, SD-WAN combines these security measures with sophisticated traffic management and threat detection capabilities.
One of SD-WAN’s standout benefits is how it can be centrally managed from the cloud. This enables easier network configuration, monitoring, and maintenance from a single interface, accessible from anywhere with an internet connection.
This centralised control simplifies network operations, reducing the need for specialised IT staff at each location. Traditional WAN solutions, like MPLS, typically require manual configurations and adjustments at multiple sites, making management more complex, time-consuming and less streamlined.
SD-WAN is highly scalable because it can use whatever bandwidth is available. It is not limited by a single line but whatever is enabled and connected to your business’s routers. This includes full-fibre, cable, satellite broadband and MPLS, offering unparalleled flexibility in how businesses configure their networks.
It can quickly and easily add new locations and allocate whatever bandwidth was agreed upon with providers under the Service Level Agreement. If this bandwidth isn’t enough, your business can simply contract yet another broadband line, and SD-WAN will incorporate it into its routing options.
Even businesses with an established MPLS system can benefit from installing an SD-WAN overlay because it can simply use the dedicated lines as another routing option for critical data transfers, leaving all non-essential data onto slower options like Starlink and OneWeb.
Even businesses just trying to remain relevant arguably need SD-WAN, as they are expected to handle increasing amounts of data generated and needed by IoT devices and AI.
SD-WAN can be easily implemented without interrupting existing services because of its virtual overlay network on top of existing infrastructure. There’s no need to rip out and replace current systems as the overlay allows for seamless integration and minimal disruption to ongoing operations.
SD-WAN is also interoperable with existing IT systems, such as project management, cybersecurity and supply chain management software, and application performance management solutions. This integration ensures comprehensive visibility and control over the entire network.
SD-WAN has multiple use cases as a wide area network (WAN) management solution. See the key features and benefits of SD-WAN to understand why these use cases are relevant.
Its main use case is for any institution with operations in multiple locations. This could be a small, medium, or large business or public institution like a hospital, university, or ministry.
SD-WAN can even negate the need for VPN solutions as it can act like one when the network is extended to remote workers. Here’s a summary of use cases:
| Use Case | Description |
|---|---|
| Enhanced Connectivity for Branch Offices | Connects multiple branch offices to the central network using lower-cost internet connections, making it easier and more affordable to expand the network. |
| Improved Application Performance | Prioritises and optimises the performance of critical applications by dynamically routing traffic based on real-time conditions for smooth and efficient operation. |
| Secure Remote Access | Provides secure and reliable access for remote workers, integrating advanced security features and optimising remote connection performance. It can negate the need for VPNs. |
| Cost Management | Reduces networking costs by leveraging various internet connections, minimising the need for expensive MPLS circuits. |
| Simplified Network Management | Centralises network management, allowing IT teams to monitor and control the entire network from a single interface, simplifying policy deployment and updates. |
| Scalable Network Infrastructure | Creates a flexible and scalable network infrastructure that can easily adapt to business growth, including adding new branches or increasing bandwidth. |
| Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity | Enhances disaster recovery and business continuity by using multiple connections and dynamically rerouting traffic to ensure continuous network availability. |
SD-WAN software is typically deployed on a centralised cloud server, as this gives plenty of benefits. However, deploying on-premises or as a hybrid model is also possible.
Let’s have a look at each possibility:
In a cloud-based deployment, SD-WAN is deployed, managed and hosted by a cloud service. This model offers ease of deployment, reduced upfront costs, and scalability, as discussed in the benefits section.
Businesses can quickly add new sites or users without significant hardware investments. It also ensures regular updates and maintenance from the service provider, ensuring the latest features and security enhancements are always in place.
SD-WAN can also be installed and managed within the company’s data centres or IT facilities, but this comes at the expense of many benefits, such as regular updates and reduced upfront costs.
However, this model provides greater control over the network and data and is ideal for businesses with specific compliance requirements or those that prefer to manage their infrastructure. It’s also more suitable for integrations with existing security and IT policies.
A hybrid SD-WAN deployment combines cloud-based and on-premises components, with some segments being managed from the cloud while others remaining on-site.
This approach offers the best of both worlds, providing flexibility and control. Businesses can leverage the cloud for scalability and ease of management while maintaining on-premises infrastructure for critical applications and data and ensuring compliance.
Companies using on-premises SD-WAN will most often have a hybrid setting, as the convenience of cloud-based software is always useful for non-critical components.
Here are the steps your business needs to follow when integrating SD-WAN:
| Step | Description |
|---|---|
| Assessment | Evaluate current network infrastructure and identify areas where SD-WAN can provide the most benefit. |
| Supervised or Unsupervised? | Evaluate where you want to integrate SD-WAN through an intermediary or directly with one of the big players. |
| Planning | Develop a detailed integration plan, including timelines, resources, and responsibilities. |
| Pilot Deployment | Start with a pilot deployment in a controlled environment to test the integration and performance. |
| Full Deployment | Gradually roll out SD-WAN across the entire network, ensuring continuous monitoring and optimisation. |
| Training and Support | Provide training for IT staff and end-users to ensure smooth adoption and ongoing support. |
Businesses might choose to work with regional or specialised managed service providers (MSPs) instead of going directly with large vendors like Cisco or Aryaka for several reasons:
SD-WAN positions your business well for the future by upgrading its interconnectivity capabilities.
Businesses need to adapt to the future of the internet, which will involve AIs and robots interconnected digitally to form the Internet of Things (IoT). The amount of data transfer to support this is expected to grow exponentially, so SD-WAN’s scalability fits the bill perfectly.
Besides this, the user experience for your employees of a well-deployed SD-WAN should work to improve your business’s efficiency. It’s secure, flexible, and less expensive than other solutions.
The top SD-WAN solutions by providers like Cisco and Palo Alto Networks are powerful yet complex. To ensure performance and meet cybersecurity compliance, a custom deployment tailored to your business and its branches is required.
Several UK-based SD-WAN Managed Service Providers (MSPs) can help you do this, including Focus Group, a Cisco-accredited MSP renowned for its expert design and deployment of multi-site networks for businesses.
Talk to our Wide Area Network experts for more information today!
The future of SD-WAN is promising, driven by several key trends and technological advancements:

SD-WAN increasingly integrates with Secure Access Service Edge (SASE) frameworks, combining network and security services into a unified, cloud-native solution. This enhances security and performance while simplifying management.

Incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning into SD-WAN solutions will enable more intelligent and automated network management, optimising performance and reducing operational complexity.

SD-WAN will play a crucial role in connecting and managing edge devices, facilitating real-time data processing and improving response times for edge applications.

Future SD-WAN solutions will continue to evolve with advanced security features, addressing the growing concerns around cyber threats and ensuring secure, resilient networks.

SD-WAN will increasingly support hybrid and multi-cloud environments, providing seamless connectivity and management across various cloud platforms and on-premises infrastructure.
Our business broadband experts answer commonly asked questions on SD-WAN:
SD-WAN benefits hybrid work by providing secure, reliable connectivity for remote and on-site employees. These employees can then access the necessary digital applications and resources. In a way, it’s like a high-performance VPN connection with a better user experience.
SD-WAN benefits IoT by providing robust and secure connectivity for numerous devices across diverse locations. It ensures reliable data transmission, optimises network traffic for real-time communication, and integrates advanced security features to protect sensitive IoT data.
SD-WAN is managed and monitored through a centralised management console, often cloud-based. This platform allows IT teams to configure, monitor, and optimise the network from a single interface.
SD-WAN and VPNs provide secure connectivity but differ in scope and functionality. See our comparison table.
SD-WAN is a sub-component of SASE (Secure Access Service Edge). SASE combines SD-WAN’s network optimisation with comprehensive cybersecurity services, such as secure web gateways, zero-trust network access, cybersecurity compliance, and cloud access security brokers. It’s the unified, cloud-native solution for networking and security.
Yes, SD-WAN can improve the performance of specific applications by prioritising their traffic, ensuring they receive the necessary bandwidth and low latency. It dynamically routes traffic based on real-time network conditions, optimising the path for critical applications like VoIP, video conferencing, and cloud services.
SD-WAN is highly secure, integrating advanced security features such as end-to-end encryption, firewalls, and secure internet gateways. Our cybersecurity features section provides more details.
SD-WAN requires ongoing support and maintenance to ensure optimal performance and security. The advantage is that being cloud-operated (typically), this can be easily done from a single interface by a single IT team.
If an SD-WAN service provider is hired alongside the software, they will handle most of the support and maintenance.
LAN (local area network) and WAN (wide area network) distinguish each other by their reach. A LAN involves tethered interconnectivity within a single property, while a WAN involves interconnectivity across a wide geographical area.
If you’re in your 30s, you must have at least heard about “LAN parties”, where gamers get together at someone’s house with their PCs to play video games like Age of Empires across a Local Area Network (LAN) formed by tethering each PC together with ethernet cables.
Businesses with multiple premises across different UK or international locations can’t physically connect all their devices to a closed LAN network. So, they must rely on a WAN (Wide Area Network) instead, which relies on sending all the data across public infrastructure.